Avelle™ Negative Pressure Wound Therapy System
Avelle™ NPWT System
Combined with 8-layered Hydrofiber® Technology, the Avelle™ Negative Pressure Wound Therapy System has proven benefits of NPWT & maintaining a optimal environment for wound healing.10
The Power of Two: Hydrofiber® Technology + Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Hydrofiber® Technology
- Locks in wound exudate and traps bacteria1-3 to help protect peri-wound skin and reduce maceration.4-5*
- Micro-contours to the wound bed, minimizing dead space where bacteria can grow.6*
- Balances wound fluid levels through gelling to maintain a moist wound healing environment.7*
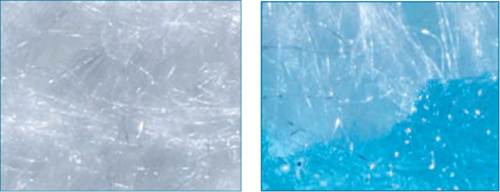
Hydrofiber® Technology Gelling Effect
NPWT - Mechanism of Action2,3
- Reduction in tissue edema
- Wound contraction via applied strain
- Increased perfusion
- Stimulation of angiogenesis
- Formation of granulation tissue
*As demonstrated in vitro.
The Avelle™ NPWT Pump
The right NPWT pump and dressing combination can make the difference in supporting wound closure and aiding patient recovery.
The disposable, single patient use Avelle™ NPWT Pump:
Delivers 80mmHg
(±20 mmHg)
Continuous therapy delivered
to the wound bed.
Clinically cost effective
Health economic solution when
compared to 7-day devices.
Up to 30-day lifespan†
Versatile therapy delivery
across care settings.
Small and portable
Ergonomic design to enhance
the patient experience.
Single button operation
Ease of use, short
learning curve.

Improving patient comfort and quality of life with the Avelle™ NPWT System
![]()
Patients can disconnect the
pump and shower with the
dressing in place whilst
maintaining NPWT
for up to 1 hour.*
![]()
Patients can stay active
whilst using the Avelle™
NPWT System to aid
recovery and rehabilitation.
![]()
Fluids are managed by the
Hydrofiber® Technology
dressing to prevent exudate
from soiling clothing.
The interactive Avelle™ NPWT Dressing
The Hydrofiber® Difference
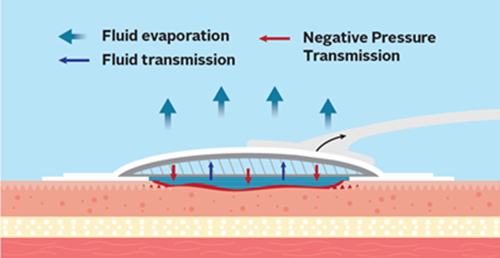
The Hydrofiber® Technology interface and inner layers within the Avelle™ NPWT Dressing are specially engineered into an apertured design to allow negative pressure transmission through to the wound.*
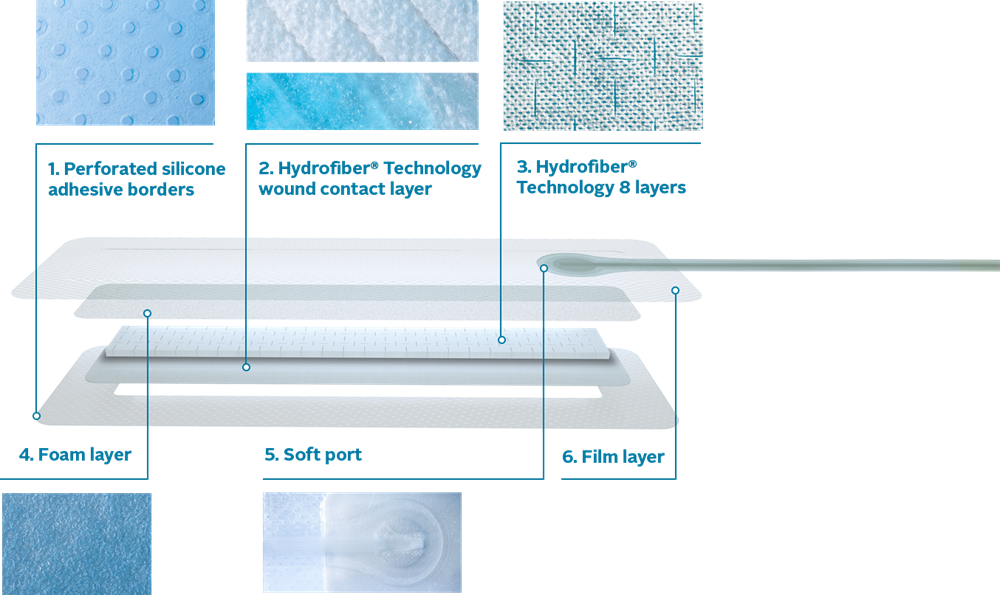
1. Perforated silicone adhesive borders
Specifically designed to secure the dressing in place while being gentle to the skin during removal.
2. Hydrofiber® Technology wound contact layer
Stitch-bonded Hydrofiber® wound contact layer gels on contact with wound fluid and is designed to maintain integrity on removal.11
3. Hydrofiber® Technology (8 layers)
Gel on contact with wound fluid and locks in bacteria within it.11,12* Fenestrations in the Hydrofiber® Technology layers are designed to promote vertical fluid movement throughout the dressing.
4. Foam layer
Aids distribution of negative pressure across the dressing and to the wound bed.
5. Soft port
Designed to minimize the risk of pressure damage.
6. Film layer
The backing film permits evaporation of exudate, aiding overall fluid handling while providing a bacterial, viral and showerproof barrier.11
- Ordering Information
The Avelle™ NPWT System is supplied in separate pump and dressing packs, allowing you to effectively manage stock and reduce wastage.
- Waring MJ, Parsons D. Physico-chemical characterisation of carboxymethylated spun cellulose fibres. Biomaterials. 2001; 22:903-912
- Newman, G.R., et al., Visualisation of bacterial sequestration and bactericidal activity within hydrating Hydrofiber wound dressings. Biomaterials, 2006. 27(7): p. 1129-39.
- Walker M, Hobot JA, Newman GR, Bowler PG. Scanning electron microscopic examination of bacterial immobilisation in a carboxymethylcellulose (Aquacel) and alginate dressings. Biomaterials. 2003; 24(5):883.-890.
- Coutts P, Sibbald RG. The effect of a silvercontaining Hydrofiber dressing on superficial wound bed and bacterial balance of chronic wounds. Int Wound J. 2005; 2(4): 348-356.
- Robinson BJ. The use of a hydrofiber dressing in wound management. J Wound Care. 2000; 9(1):32-34.
- Jones S, Bowler PG, Walker M. Antimicrobial activity of silver-containing dressings is influenced by dressing conformability with a wound surface. WOUNDS. 2005; 17(9): 263-270.
- Parsons D, Bowler P, Myles V, Jones S. Silver antimicrobial dressings in wound management: A comparison of antibacterial, physical and chemical characteristics. Wounds. 2005; 17: 222-232.
- Borgquist O, Gustafsson L, Ingemansson R, Malmsjo M, 2009, Tissue Ingrowth Into Foam but Not Into Gauze During NPWT, Wounds 2009; 21(11):302–309.
- Malmso M, Borgquist O. NPWT setting and dressing choices Made Easy. Wounds International 2010; 1(5).
- Bishop SM, Walker M, Rogers AA, Chen WYJ. Moisture balance: optimising the wound-dressing interface. J Wound Care. 2003; 12:125-128.
- Assessment of the in-vitro properties Avelle™ Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Dressing. WHRI4520 MS128. Data on file. 2015. ConvaTec.
- HFM-2015-017. Data on file. 2015. ConvaTec Inc.
*As demonstrated in-vitro
†Battery change may be required during pump lifetime.